
Our Product and Engineering teams are rolling into the harvest of a bumper crop of new features. It’s time for another fresh batch of exciting capabilities newly available in the replicated platform. Check out the recently shipped features and release highlights for September 2023 below.
What’s New for Compatibility Matrix (BETA)
OpenShift, GKE, kURL and HelmVM added to the Compatibility Matrix
The replicated Compatibility Matrix helps you provision customer-representative environments for release testing. Compatibility Matrix can now create an OpenShift (OKD 4.13) server as part of the matrix, which is exciting given how popular OpenShift is in the market. See a quick video of creating an OpenShift cluster from the CLI. The video first shows running “replicated cluster version” to see available distributions and versions. Then “replicated cluster create is used to specify an OpenShift 4.13.0-okd cluster being queued and quickly prepared for testing.
Similarly, Compatibility Matrix can now create a GKE (1.27, 1.26, 1.25) server as part of the matrix. Watch an example of creating a GKE 1.27 cluster from the CLI.
And Compatibility Matrix can now create a HelmVM 1.27 server as part of the matrix. Check out this recording of creating a HelmVM 1.27 cluster from the CLI.
Finally, you can now specify a valid kURL version to get a single node kURL installation. If you have a KOTS application and support both embedded and existing clusters, you can now set up a workflow in CI to validate against your supported distributions.
Taken together, these represent a massive increase in coverage and access to common customer environments, all at your fingertips. Contact us if you’d like to learn more.
Create a test cluster separate from promoting a release
We have added a replicated cluster prepare command to create a cluster without promoting a release to a channel. So you can deploy applications for compatibility testing in your development workflow without the need to create and promote releases while you are still iterating. It also uses the new customer type `test` to create licenses for iterating during development. See also the reference documentation.
KOTS and SDK changes are now tested via Compatibility Matrix
A bit of an inside look, but we’re excited that now we test the viability of our own KOTS releases on Compatibility Matrix. This gives us more confidence that you (and your end customers!) will not hit unexpected issues with KOTS and SDK on common cloud providers’ services and other distributions, like kind, k3s, EKS, GKE, and OpenShift clusters.
What’s New for Vendor Portal
Send custom metrics to Vendor Portal (BETA)
Custom metrics is one of our most requested feature enhancements for Vendor Portal. You can now send your own custom telemetry via KOTS (available with KOTS v1.102.0) or the replicated SDK (available with SDK v1.0.0-beta.5). These metrics are then visible via their respective Instance Details pages. See our custom metrics docs or watch this short video showing custom metrics in Instance Insights.
Test slack webhooks for notifications
Slack is a great way to stay informed with Instance Telemetry Notifications, but you might want to test the Slack integration works as expected before sending actual live event notices out. Now, you can check if the Slack webhook is valid without needing to trigger a real notification from a live instance. This should improve the usability of notifications and make it easier to correctly configure behavior.
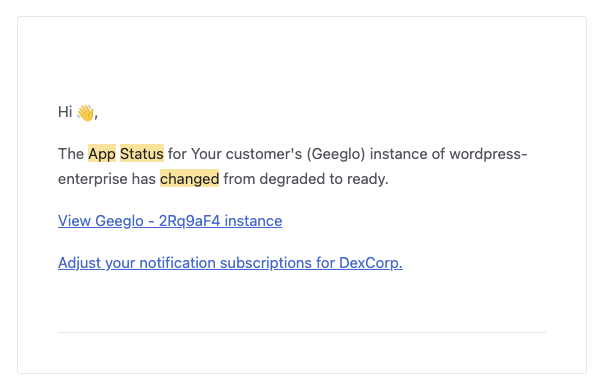
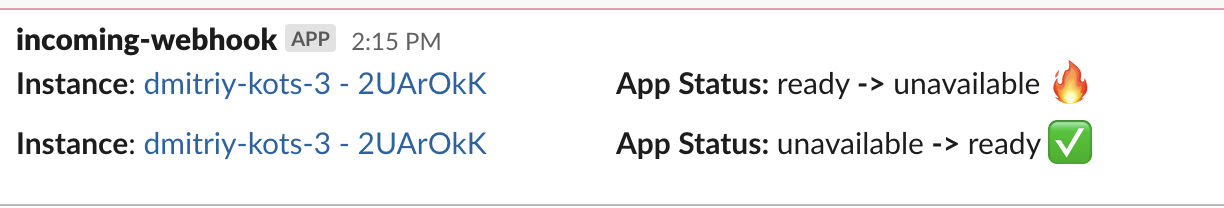
Improved customer notifications messaging
Instance Telemetry Notifications that are rendered in your email and slack inboxes now have some nice additions like emojis, more context, better wording, and links to manage or disable notifications. The use of emoji especially helps people quickly visually identify various status changes to their app instances.
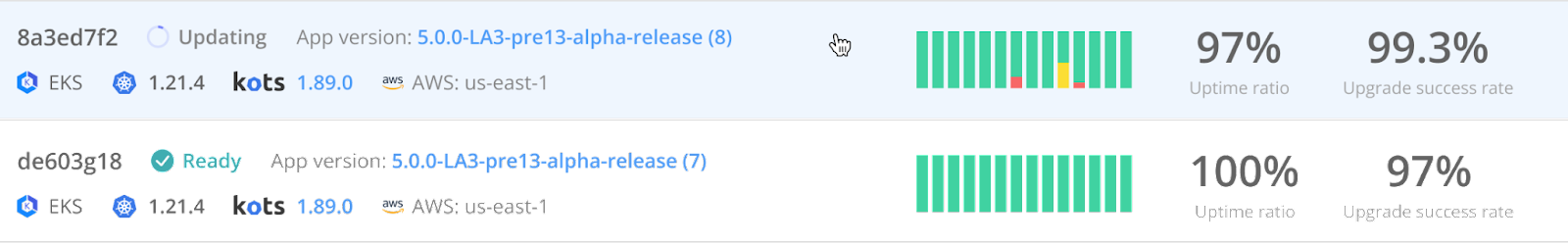
Real-time updates on the customer reporting page
When customer instances change or new instances are launched, the Customer Reporting page will now update dynamically, without requiring a refresh. This delivers a better user experience overall.
What’s New for KOTS and the replicated SDK
replicated SDK now compatible with Helm and CD tools like ArgoCD and Pulumi
In addition to standard helm deployments via `helm install` or `helm upgrade`, the SDK can now also be installed successfully alongside Helm chart deployments that leverage `helm template` then `kubectl apply` to install/update (as of replicated SDK v1.0.0-beta.5). Some popular enterprise continuous delivery tools, such as ArgoCD and Pulumi, deploy Helm charts by running `helm template` then `kubectl apply` the generated manifest rather than doing a `helm install` or `helm upgrade`. Given the ubiquity of these tools, we wanted to ensure the SDK could support installing successfully alongside the application in this type of deployment model. There our some functionality limitations when deploying in this mode, which are outlined here.
replicated SDK support extended to include OpenShift (v0.0.1-beta.4)
We added the ability to detect if the cluster is OpenShift, which applies the `restricted-v2` security context by default, and has very specific requirements about dynamically generated ids. This nicely complements the ability to test OpenShift with Compatibility Matrix.
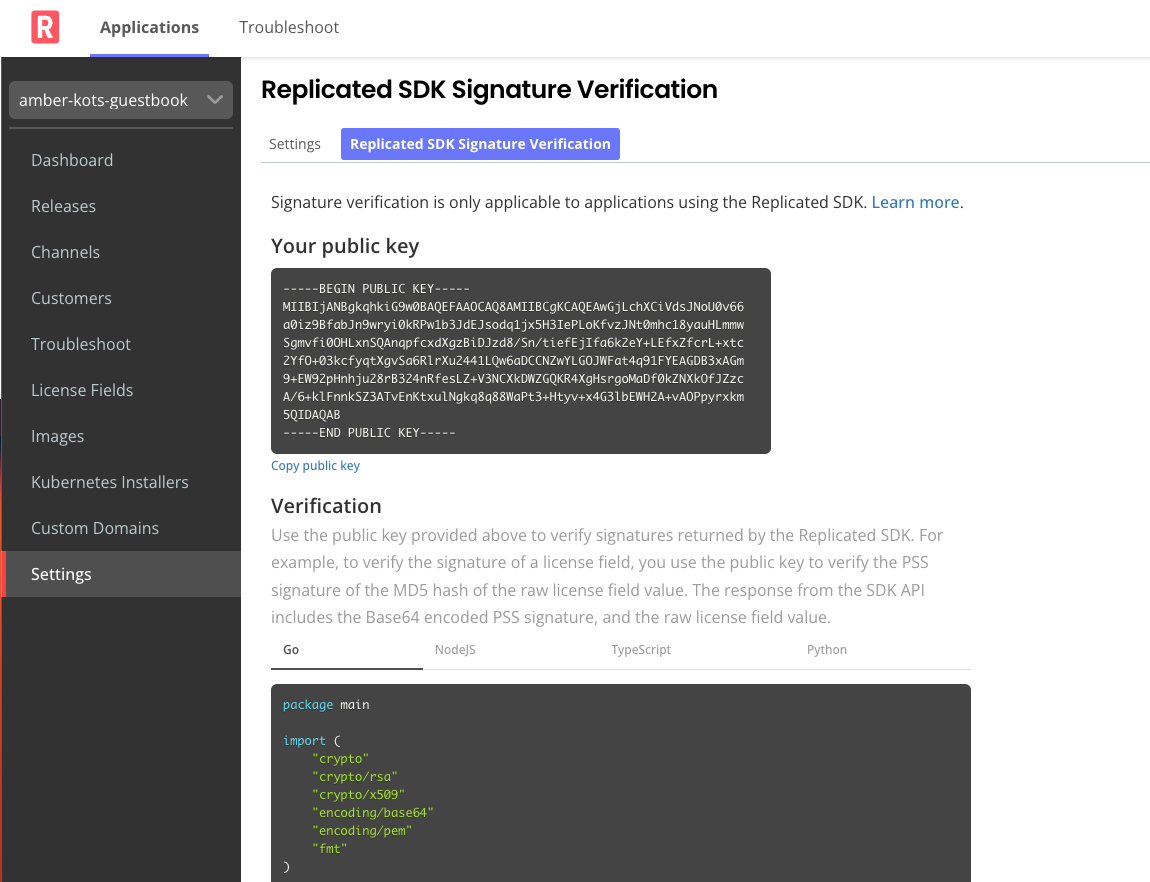
The SDK signature verification page is now available to everyone in Vendor Portal
replicated recommends that when you use the replicated SDK API to return license field values you should also use signature verification to ensure the integrity of each license field relied on by your application. The docs on how to do this are live, and the Vendor Portal page is now accessible to anyone wanting to try out an SDK integration.
replicated SDK now returns app status in the /app/info endpoint response (v0.0.1-beta.2)
Previously the app status info was just stored in the SDK logs, making it a little more work to find. Enabling this info to also be retrieved from the app info endpoint makes it easier to build collectors and analyzers for troubleshooting, and allows you to more easily retrieve this info for use in your application or other observability tooling.

What’s New for Embedded Kubernetes
Reliability of storage migrations improved
When PVC and Object Storage migrations are required during an upgrade due to kURL installer spec CSI changes, those migrations will now run before Kubernetes itself is upgraded (if relevant) in order to improve reliability of these critical storage migrations.
What’s New for Customer Reliability Engineering
Collect helm install history (Troubleshoot v0.71.1)
This new collector will collect details about helm releases and their history. See the Troubleshot Docs for more information.
What’s New for Product Documentation
Release notes available for the replicated SDK
When integrating the Beta replicated SDK, you now have an easier way to consume information about the latest improvements and fixes available. See the replicated SDK release notes.
New topics about managing applications
A new Applications section in the main sidebar includes information about how to manage applications (create, delete, get the app slug) and about the application Settings page in the vendor portal. Whereas this information existed in the documentation previously, it was spread across different topics and sections, making it difficult to find. Now, it’s all grouped together in a more intuitive location.
Recommendations for integrating replicated CLI commands & the compatibility matrix with CI/CD pipelines
Two new topics about CI/CD (an overview as well as more detailed, recommended workflows) provide guidance for incorporating replicated CLI commands with your CI/CD pipelines. These topics include both high-level and step-by-step recommendations that give you a starting place and help set you up for long term success.
That’s it for the September release highlights!
Want to learn more about these new features and what replicated does to help vendors with modern apps in customer-managed environments? We would love to show you -- click here to schedule a demo.